NEJM Trial on Mucoactive Therapies in Bronchiectasis: Structural Reassessment of Clinical Value
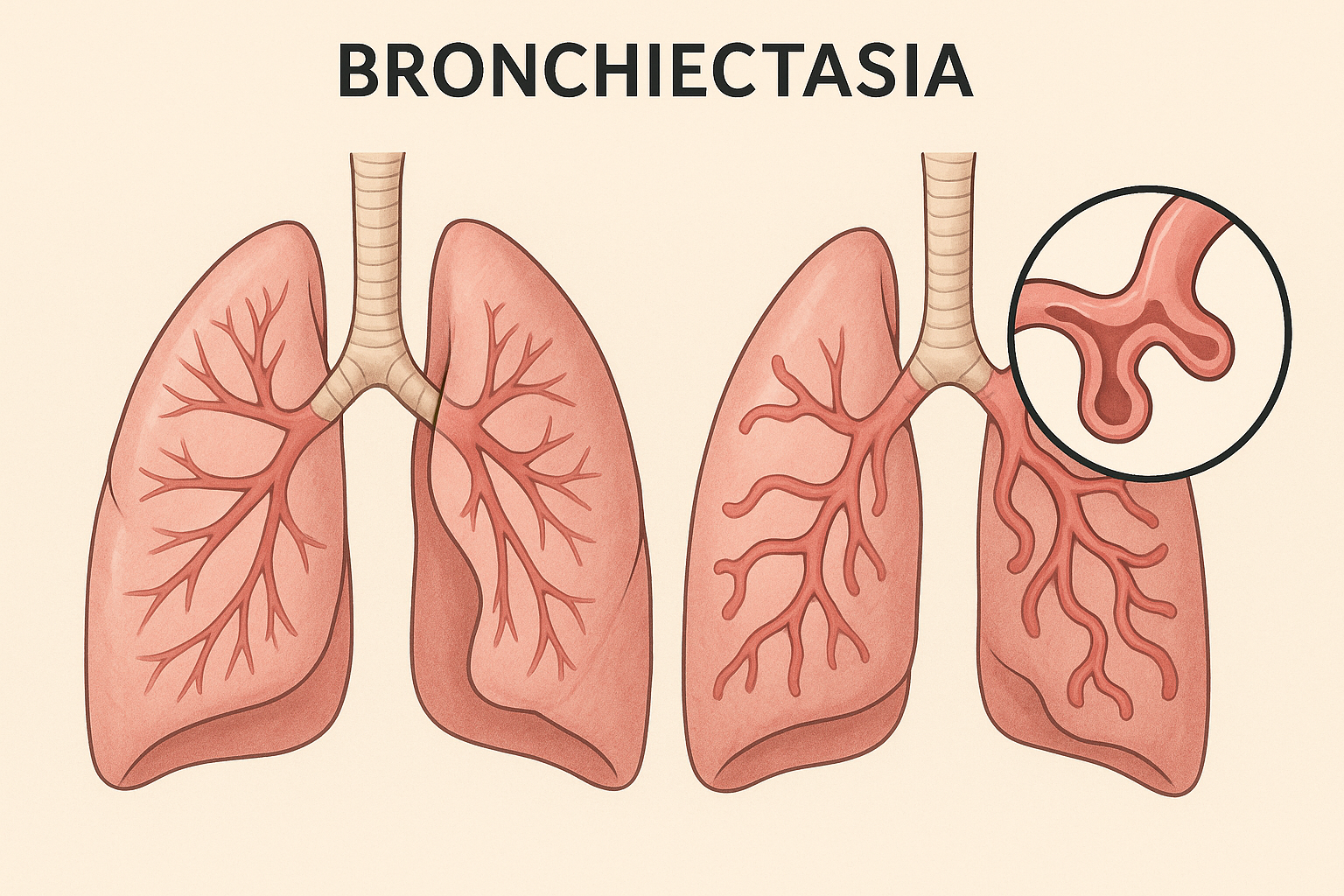
Trial at a glance (CLEAR, NEJMoa2510095).
Multicenter UK, 2×2 factorial, n=288, 52-week follow-up. Interventions: 6% hypertonic saline (inhaled) and carbocisteine (oral) vs standard care.
Primary outcome: annualized exacerbations — no significant reduction (adj. Δ: saline −0.25; carbocisteine −0.04).
Secondaries: no consistent benefit in QoL, lung function, or time-to-exacerbation. Safety acceptable.
Implication.
Guideline habit of universal mucoactive use in non-CF bronchiectasis is structurally weakened; shift toward selective, symptomatic use rather than routine prescription.
Annex Snapshot — Technical Evidence Base (Key Points)
Inhaled Heparin: An Old Anticoagulant Emerging as a New Weapon Against Severe Respiratory Infections
What’s new. A multinational meta-trial (eClinicalMedicine, 2025) found nebulized unfractionated heparin cut the combined risk of intubation or death by ~50% in hospitalized COVID-19 patients versus standard care—reigniting interest in a cheap, stockpiled therapy.
Why it matters. Current tools are fragmented (early antivirals, broad steroids, pricey biologics). Inhaled heparin concentrates action in the lungs with minimal systemic exposure, making it attractive for low- and middle-income settings and surge waves.
How it works (multi-pathway).
Anticoagulant: counters pulmonary microthrombosis.
Anti-inflammatory & endothelial protection: stabilizes the alveolar–capillary barrier.
Antiviral decoy: can bind spike proteins and impede entry.
Safety/unknowns. Generally reassuring with inhalation (lower systemic absorption → lower HIT risk), but dose, schedule, and bleeding surveillance need Phase III confirmation.
Mini-Annex (snapshots).
Nexiguran Ziclumeran Gene Editing in Hereditary ATTR with Polyneuropathy
The NEJM trial of nexiguran ziclumeran (NTLA-2001) marks the first demonstration of systemic in vivo CRISPR editing in humans. By targeting hepatic TTR production, patients with hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis achieved >90% median serum TTR knockdown and stabilization of neuropathy scores. While safety signals were generally favorable, the study’s early-phase design leaves key uncertainties: attribution of serious adverse events, long-term off-target effects, and the consequences of lifelong TTR silencing. Beyond ATTRv-PN, this trial symbolizes a turning point—patients act simultaneously as treatment recipients and pioneers in proving the feasibility of permanent gene editing for chronic disease.
Permethrin-Treated Baby Wraps: An Experimental Shield Against Malaria
The NEJM trial on permethrin-treated baby wraps reveals both the promise and the peril of chemical vector control in Africa. While the wraps reduced malaria incidence among infants, their long-term use risks ecological toxicity and accelerated resistance in Anopheles mosquitoes. In contrast, the dojo loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus) offers a bioeconomic pathway: natural larval predation, improved community nutrition, and sustainable resilience. The future of malaria control will not be decided by chemistry alone, but by whether we choose dependency or ecological sovereignty.
FDA Blocks Biogen’s High-Dose Spinraza in the U.S.: A Regulatory Setback Driven by Manufacturing Controls
On September 23, 2025, the FDA issued a Complete Response Letter (CRL) rejecting Biogen’s high-dose Spinraza submission, not due to safety or efficacy, but because of deficiencies in Module 3 (CMC). This dossier, the cornerstone of manufacturing integrity, failed to convince regulators that the higher-dose formulation could be produced consistently and reliably at scale. The rejection highlights a structural miscalculation: Biogen’s decision to prioritize speed under commercial pressure, while leaving critical documentation incomplete. It is a reminder that in today’s regulatory landscape, the ultimate gatekeeper of therapeutic progress is not clinical promise, but manufacturing rigor.
Low-Dose Aspirin in PI3K-Altered Colorectal Cancer: From Observational Hints to Randomized Proof
From willow bark to genomic oncology, aspirin’s journey spans centuries. In 1763, Reverend Edward Stone tested the bitter powder of willow bark to relieve fever, unknowingly isolating the foundation of modern pharmacology. Two centuries later, the same compound re-emerges in precision medicine: low-dose aspirin, repurposed not for the masses but for a genetically defined subset of colorectal cancer patients carrying PI3K-pathway mutations. The continuity is striking—what began as rustic empirical observation now stands as randomized evidence in The New England Journal of Medicine. Yet the paradox remains: a pill that costs less than a coin can alter the trajectory of cancer recurrence, while at the same time demanding restraint, lest its indiscriminate use lead to hemorrhagic harm.
Tylenol, Pregnancy, and Autism Risk: Between Policy Shock and Scientific Ambiguity
Acetaminophen, long perceived as the “safest” option for pain and fever in pregnancy, is now at the center of regulatory and scientific controversy. The FDA’s recent announcement acknowledges a possible association between prenatal exposure and neurodevelopmental disorders, while new mechanistic studies point to hormonal disruption, epigenetic silencing, and oxidative stress in the developing fetal brain. The debate illustrates a deeper epistemic tension: how far precautionary policy should go when evidence is observational, contested, but biologically plausible.
Keytruda SC Approval: Alteogen’s ALT-B4 Transforms Oncology Administration into a One-Minute Therapy
The FDA approval of Keytruda QLEX™, the first subcutaneous formulation of pembrolizumab co-developed by Merck and Alteogen, marks more than a convenience upgrade. It is the structural reconfiguration of oncology: shifting from one-hour IV infusions to two-minute injections, from tertiary hospitals to community clinics, and from milestone payments to recurring global royalties. For Merck, it extends dominance beyond the 2028 patent cliff; for Alteogen, it validates a single Korean enzyme as the indispensable backbone of the world’s best-selling cancer drug.
Avian Influenza Returns to Minnesota: Turkey Industry Caught Between Containment and Vaccine Hopes
Avian influenza has returned to Minnesota, exposing once again the structural fragility of the poultry trade. Nearly 20,000 turkeys were culled in Redwood County, a reminder that lasers and biosecurity can delay but not prevent outbreaks. Farmers now pin their hopes on vaccination, yet no vaccine currently matches the dominant strain, and timelines remain uncertain.
This report delivers two layers of analysis: the main body concludes with the BBIU Opinion for readers seeking clarity and judgment, while extended Annexes provide definitions, economic models, and global trade context for those requiring full traceability.
FDA Warning on Imported Cookware: Regulation Exists, Enforcement Fails
In August 2025, the FDA issued a safety alert on imported cookware that leaches lead into food. This is not a case of weak regulation — U.S. law explicitly bans lead in food-contact surfaces. The real failure lies in global enforcement: contaminated products entered the retail chain, and in one case the importer could not even be identified, blocking a recall.
Lead poisoning, or saturnism, is an ancient disease in a modern disguise. Its symptoms are silent, its diagnosis depends on clinical suspicion, and its victims are often children, pregnant women, and low-income households. What was once the occupational disease of miners now reflects a deeper fragility: law without traceability is powerless, and globalization re-imports the toxic risks it once expelled.
Oral Semaglutide 25 mg – OASIS 4 Trial
The OASIS-4 trial introduces oral semaglutide 25 mg as a mid-tier obesity therapy, achieving a 13.6% weight reduction at 64 weeks in non-diabetic adults. While the oral route promises broader patient acceptance and reduced costs compared with injectables, the absence of serious adverse event reporting leaves critical gaps in safety transparency. When contrasted with CagriSema — which delivered ~20% weight loss in non-diabetic cohorts and ~13.7% in diabetic patients — OASIS-4 appears less a clinical breakthrough than a commercial positioning maneuver. Novo Nordisk is constructing a strategic portfolio ladder: high-efficacy injectables, high-dose oral, and now an intermediate oral dose to normalize GLP-1 use as a daily pill. This shift democratizes access but raises structural risks of adherence, efficacy trade-offs, and long-term dependency.
Pharma’s Domestic Reinforcement Wave: $5B Eli Lilly Virginia Plant and the $350B Pledge Cascade
Eli Lilly’s $5 billion Virginia plant is not an isolated corporate expansion, but part of a $350 billion wave of U.S. biopharma reshoring triggered by tariff threats and strategic signaling from Washington. While Big Pharma secures high-margin biologics inside U.S. borders, the chemical backbone of medicine—antibiotics, insulin, heparin—remains dangerously dependent on India and exposed to disruption. BBIU’s position is clear: biologics sovereignty protects profits, but API sovereignty protects lives.
Comprehensive Proposal: Pharmacological Training for Presbyopia
Presbyopia is not merely an inconvenience of aging; it is the structural stiffening of the eye’s optical system. Unlike glasses or surgery, which correct vision externally, pilocarpine engages the eye’s own ciliary muscle, effectively acting as pharmacological training for accommodation. The addition of diclofenac provides the anti-inflammatory shield that allows this “rehabilitation” to be sustainable in daily life.
The Phase 3 trial is therefore more than a test of efficacy: it is an experiment in restoring biological function. By comparing four groups—combination, pilocarpine alone, diclofenac alone, and placebo—we can determine not only whether the therapy works, but also whether it is tolerable over long-term, chronic use. This design mirrors real-world conditions, with the added safeguard of a rescue option after Day 60, reflecting how patients would behave outside the trial.
Trump’s Pharmaceutical Advertising Crackdown: Full Picture & Patient Implications
Pharmaceutical advertising in the U.S. changed radically after 1997, when the FDA’s “adequate provision” rule allowed 30-second TV spots to highlight benefits and hide risks. Over time, Marketing & Sales eclipsed Medical Affairs, eroding the ethical filter that should have protected patients.
Trump’s new crackdown is not a ban but a structural correction: forcing risk disclosure, closing the loophole, and confronting an industry that converted medicines into consumer products.
Evidence is clear: advertising inflates prescriptions, drives polypharmacy, and shifts demand toward expensive branded drugs. The billions spent annually on ads are baked into drug prices, fueling healthcare inflation. The real danger ahead is not repeal but displacement: pharma may migrate aggressively to digital platforms, where regulation is weak and manipulation even more insidious.
For patients, this measure is necessary. It restores part of the integrity that the industry itself abandoned. Medicines are not sneakers or soft drinks. Selling them through distorted advertising was always a deviation.
Marburg Virus Disease in Rwanda (2024)
The Marburg virus, one of the most lethal pathogens known to medicine, exposes the structural fragility of global health systems. With mortality rates reaching up to 80%, its pathophysiology —endothelial destruction, hepatic necrosis, and immune collapse— creates a narrow therapeutic window. Traditional supportive care is insufficient; innovative interventions must be considered.
Monoclonal antibodies, long confined to oncology, emerge as a viable countermeasure. By reversing T-cell exhaustion and re-arming NK cytotoxicity, they could tilt survival even in viral hemorrhagic fevers. Combined with interferon gamma in early stages, they offer a plausible immune recalibration strategy.
Beyond the clinic, the implications are ethical and geopolitical. Patients facing near-certain death deserve transparent access to experimental therapies. Cold-chain precedents from COVID-19 prove logistical feasibility. Expanded indications could also lower costs and extend patent lifespans, transforming mAbs from niche cancer products into dual-use biodefense assets.
Marburg reminds us that medicine cannot remain siloed. What was once “too dangerous” in cancer may be ethically mandatory in outbreaks where mortality is overwhelming. This shift reframes monoclonals as not only instruments of cancer therapy, but as strategic tools of survival and global security.
Ribociclib: From Phase I Dose Definition to Adjuvant Positioning — Clinical Trajectory and the Transparency Dilemma
Signals of resistance — documented years ago in FELINE and related preprints — remain underacknowledged in official narratives. The true credibility of adjuvant CDK4/6 therapy will not be secured by hazard ratios alone, but by full transparency on resistance, toxicity, and the patient experience. Only then can ribociclib’s full arc — from safe dose definition in phase I, exploratory validation in phase II, to pivotal MONALEESA survival gains and adjuvant confirmation in NATALEE — be properly understood as both achievement and unresolved dilemma
Adjuvant CDK4/6 Inhibitors in Early Breast Cancer: Benefit, Cost, and the Emerging Paradox of Resistant Relapses
Adjuvant use of CDK4/6 inhibitors in early breast cancer brings a paradox: modest reductions in recurrence at the cost of profound human and economic burdens. Abemaciclib prevents one relapse for every ~14 patients treated; ribociclib for every ~32. Yet the price is measured not only in millions of dollars per event avoided, but also in years of fatigue, gastrointestinal distress, liver toxicity, disrupted family life, and the silent erosion of mental health. For many survivors, the treatment does not end with the last pill—it leaves behind scars that shape work, relationships, and future prospects. Families facing this decision must balance time gained against suffering endured, with no certainty yet that overall survival is extended.
Sanofi’s $13B Erosion: Amlitelimab’s Trial Results and the Pipeline Dilemma
Sanofi’s $13B market loss following amlitelimab’s Phase III results reflects not a scientific failure, but a mismatch between biology and expectations. Unlike Dupilumab’s rapid downstream blockade of IL-4/IL-13, amlitelimab acts upstream at the OX40L–T cell axis, requiring more time to reshape immune responses. The COAST-1 trial met its primary endpoints using vIGA-AD, a more rigorous scale than Dupilumab’s IGA, and included adolescents as well as adults, making direct comparisons misleading. Efficacy at 24 weeks was statistically significant (21–23% vs. 9% placebo), safety was favorable, and long-term potential extends to synergy in atopic dermatitis and applications in autoimmune disease. The market judged amlitelimab as a weaker Dupixent; in reality, it is a different drug with a different biological logic.
One Dose versus Three Doses of Benzathine Penicillin G in Early Syphilis (NCT03637660, NEJM 2025)
The NEJM 2025 trial (NCT03637660) has overturned a decades-old convention in syphilis treatment: a single 2.4M unit dose of benzathine penicillin G proved noninferior to the traditional three-dose regimen. This finding comes at a time when syphilis cases are resurging globally—and in South Korea, where nearly 2,800 cases in 2024 were concentrated among young men, reinforcing both a clinical and structural vulnerability. The lesson is clear: sufficiency, not redundancy, ensures resilience. Read more here.
Beta-Blockers Post-MI: Sex-Specific Evidence and the Collapse of a Universal Dogma
For decades, beta-blockers were given automatically after every heart attack. Modern evidence now shows they are not always necessary: they remain vital for patients with weakened heart function or arrhythmias, but offer no universal benefit. The future of cardiac care lies in personalized treatment, not one-size-fits-all dogma.