Regulatory Accountability Collapse Under Event-Based Truth
The FDA’s recall framework still treats quality failure as a sequence of isolated events rather than as an accumulating signal of manufacturer reliability. The Glenmark case exposes this structural blind spot. A recall can exist administratively without becoming epistemically relevant, while more than a decade of recurrent quality deviations remains unintegrated into regulatory truth.
This is not an enforcement failure. It is a memory failure.
The legacy p-value and gate-validation paradigm was never designed to price recurrence, provenance opacity, or long-run execution drift. Bayesian regulation creates the technical capacity to correct this—but only if accountability is encoded by design. Without historical performance as a formal prior, Bayesian tools risk accelerating belief updates without increasing truth.
In a belief-governed regulatory era, accountability cannot remain episodic. Reliability must be inferred over time, across products, sites, and people—or regulatory stability becomes a surface illusion sustained by deferred accumulation of risk.
FDA - Depth as Regulatory Truth
The FDA’s draft guidance on Minimal Residual Disease (MRD) and Complete Response (CR) in multiple myeloma marks a decisive shift in how regulatory truth is constructed. This is not an oncology-specific refinement, but a structural reallocation of epistemic burden. As overall response rates saturate and lose discriminative power, approval credibility migrates toward depth-based biological resolution governed by assay validity, data integrity, and methodological coherence.
Under this framework, accelerated approval is no longer constrained by trial size or population-level separability, but by the precision and governance of measurement systems. MRD does not relax regulatory standards; it relocates risk. The system preserves speed by embedding conditionality into assays rather than statistics, extending epistemic exposure across the product lifecycle. In this regime, regulatory advantage accrues not to those who generate deeper responses fastest, but to those who can sustain measurement coherence over time.
New FDA epistemic approach - From Living Products to Living Belief
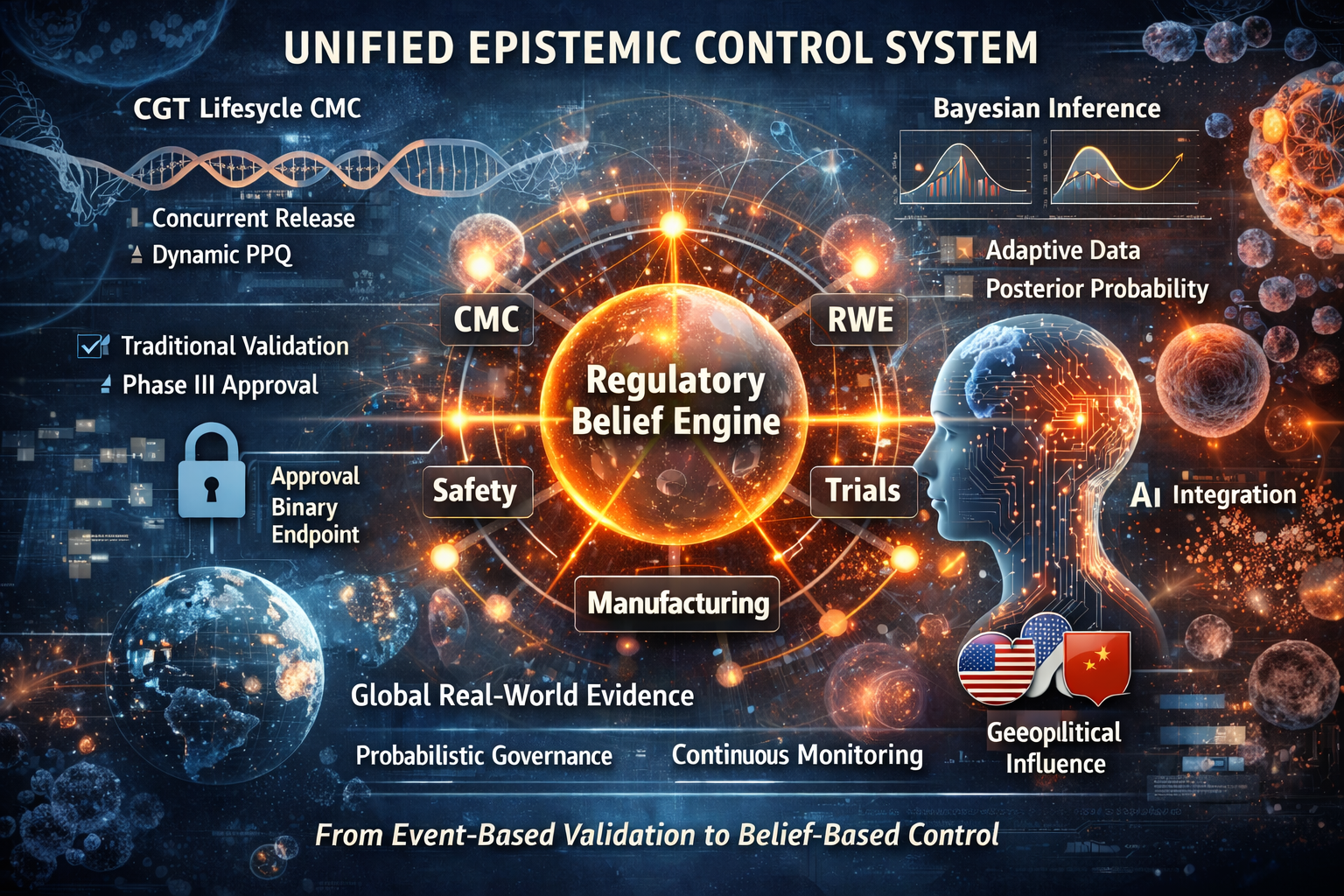
In 2026, the FDA ceased to regulate drugs as finished objects.
Through the convergence of CGT lifecycle manufacturing control and Bayesian regulatory inference, it began to regulate them as living epistemic systems.
Cell and gene therapies no longer achieve truth through validation events. Their identity is sustained through continuous manufacturing governance, global data streams, and probabilistic belief updating. At the same time, Bayesian methodology dissolves the finality of Phase III, replacing hypothesis rejection with a permanently evolving posterior probability of therapeutic reality.
These two shifts form a single regulatory architecture: a unified epistemic control system in which manufacturing stability, clinical evidence, and real-world outcomes collapse into one continuously updated regulatory belief.
What appears as flexibility is in fact a structural concentration of power.
Regulatory authority now resides in those who control data, registries, and biological continuity across time.
In this regime, molecules are not approved.
They are continuously believed.
Cardiovascular Disease: LDL Lower Is Better—At What Structural Cost?
The expansion of PCSK9 inhibition into primary cardiovascular prevention marks a critical inflection point in modern lipid management. While statistical efficacy has been demonstrated, the structural question remains unresolved: whether aggressive LDL suppression translates into proportional system-level value.
This analysis demonstrates that the observed 1.8% absolute risk reduction comes at the cost of escalating pharmacological mass, subcutaneous delivery burden, and unpriced non-cardiovascular uncertainty—particularly in older, polymedicated populations where interaction density, not single-drug toxicity, defines real-world risk.
Under ODP–DFP scrutiny, PCSK9 inhibition emerges not as a failure of innovation, but as a signal of saturation: a state where biochemical precision outpaces clinical leverage, and where guideline legitimacy no longer guarantees public health efficiency.
This report does not dispute efficacy.
It audits proportionality.
Oralization at Scale and Deferred Risk Disclosure
The rapid expansion of GLP-1 receptor agonists is no longer an efficacy story.
It is an exposure-architecture story.
Between mid-2025 and early 2026, the GLP-1 system crossed a structural threshold: oralization removed friction, normalized chronic use, and accelerated population-scale exposure faster than regulatory codification could adapt. As a result, low-frequency but high-impact risks—previously buffered by injectable gating, specialist oversight, and limited uptake—have begun to surface as structurally relevant signals rather than isolated anomalies.
The absence of new label warnings on irreversible visual impairment, despite emerging observational data and pharmacovigilance reports, does not negate risk. It reveals a temporal asymmetry between evidentiary horizons and real-world deployment. In such systems, regulatory silence functions less as reassurance and more as a lagging indicator.
This analysis demonstrates how early structural signals—dismissed when incidence appears small—become legible only once scale validates them. The core risk is not molecular novelty, but the geometry of exposure itself.
Regulatory Truth Rewritten — The FDA’s Bayesian Turn as Structural Reallocation of Epistemic Power
From Hypothesis Rejection to Belief Governance under ODP–DFP Stress
For more than half a century, FDA approval has not meant that a drug was true.
It meant that disbelief could no longer be sustained.
Under the frequentist regime, regulators never asserted that a therapy worked; they merely rejected the hypothesis that it did not. This preserved legal defensibility—but it also displaced epistemic responsibility. Clinical development proceeded inside a statistical fiction where “passing” replaced “being true.”
The FDA’s January 2026 draft guidance on Bayesian methodology ends that fiction.
By authorizing Bayesian primary inference in pivotal trials, the Agency has redefined regulatory truth as a quantified belief state—a posterior probability built from biology, historical trials, external datasets, and real-world evidence. Approval is no longer an event. It is a continuously updated belief about clinical reality.
This shift is not philosophical. It is structural.
Small populations, globalized execution, China-centered trial ecosystems, and exploding real-world data volumes have made hypothesis-based validation obsolete. In response, the FDA has converted its regulatory engine from event-based adjudication to belief governance.
Whoever controls data now controls truth.
And in a Bayesian FDA, truth is no longer declared—it is computed.
Strong Clinical Signal, Inconsistent Public Disclosure in an NEJM Phase III Trial
A Phase III oncology trial published in The New England Journal of Medicine reports a strong efficacy signal for sacituzumab tirumotecan in EGFR-TKI–resistant non-small-cell lung cancer. The biological signal is coherent and statistically robust.
However, all reported data originate from clinical execution exclusively within China. No independent external verification, multinational replication, or cross-jurisdictional regulatory stress testing has yet occurred. Despite this, the study has been elevated to CME material, accelerating educational normalization ahead of full auditability.
With the asset subsequently licensed out to MSD, the program now enters a phase where external verification is unavoidable. Until consistent data emerge outside China, the results should be interpreted as jurisdiction-bound rather than globally generalizable.
This analysis does not dispute efficacy. It audits portability.
High-Dose Rifampin and the Structural Limits of Antibiotic Escalation in Tuberculous Meningitis
The HARVEST trial did not fail because rifampin is ineffective, nor because tuberculosis therapy is misguided. It failed because it tested pharmacologic escalation at a stage where tuberculosis is no longer primarily a drug-limited disease. Once tuberculous meningitis is clinically established, the dominant determinants of outcome shift away from antimicrobial exposure toward systemic disease stage, compartmental constraints, and host-driven inflammatory and vascular injury within the central nervous system. Increasing rifampin dose increased pharmacologic force, but the disease system could no longer convert that force into survival.
Strong Clinical Signal, Inconsistent Public Disclosure
A Phase 3 trial published in The New England Journal of Medicine reports unusually large efficacy gains for disitamab vedotin combined with toripalimab as first-line therapy in HER2-expressing advanced urothelial carcinoma. Median progression-free survival and overall survival more than doubled relative to platinum-based chemotherapy, with a lower incidence of high-grade adverse events.
However, independent reconstruction of the trial’s execution reveals material disclosure inconsistencies. The published article attributes the dataset to a single registered Phase 3 study (NCT05302284), yet the corresponding ClinicalTrials.gov record lists the study as active/recruiting, with only two participating centers in Beijing and no posted results. In contrast, sponsor press releases describe the same trial as completed, multicenter, conducted across 74 sites in China, with 484 patients enrolled and mature survival outcomes available.
These divergences—across peer-reviewed publication, trial registry, and corporate communications—do not negate the reported efficacy signal. They do, however, constrain external verification of trial scale, timing, and data provenance based on publicly available records. As a result, confidence in global portability rests not on biological plausibility, but on unresolved gaps in disclosure alignment.
When Assumptions Replace Verification: Influenza Vaccine
DANFLU-2 and GALFLU do not represent conflicting scientific truths.
They represent a shared epistemic omission.
Both studies operate within a framework where influenza vaccine effectiveness is treated as axiomatic rather than empirical. Incremental differences between formulations are measured, while the foundational causal chain—season-specific immunogenicity, functional neutralization, and absolute protection versus non-vaccination—is never re-established.
This is not a failure of data access, nor of statistical technique. It is a failure of epistemic discipline, embedded in a system optimized for continuity rather than verification.
When assumptions replace verification, statistical significance becomes narrative stabilization—not scientific confirmation.
CAR-T Safety Architecture and the FDA’s Single-Trial Pivot
CAR-T therapy is not a static intervention — it is a living system whose risk geometry unfolds across time.
The first six months capture only the acute phase: cytokine storms, cytopenias, and early neurotoxicity.
But the structural risk expression begins later.
Between months 6 and 24, the biological vectors that govern long-term safety — clonal evolution, genomic misintegration, chronic immunosuppression, and secondary malignancy pathways — become visible for the first time. This is the true horizon where CAR-T reveals whether its therapeutic profile converges toward stability or drifts into delayed oncogenesis.
A regulatory framework that evaluates CAR-T at 12 months measures only the absence of early collapse — not the presence of long-term integrity.
Time is not a variable to be controlled; it is the primary diagnostic instrument.
BBIU’s conclusion is unequivocal:
No CAR-T therapy can be declared structurally safe without >24 months of continuous observation and peripheral CAR-T tracking. Anything less is epistemically incomplete.
The FDA’s Single-Trial Pivot
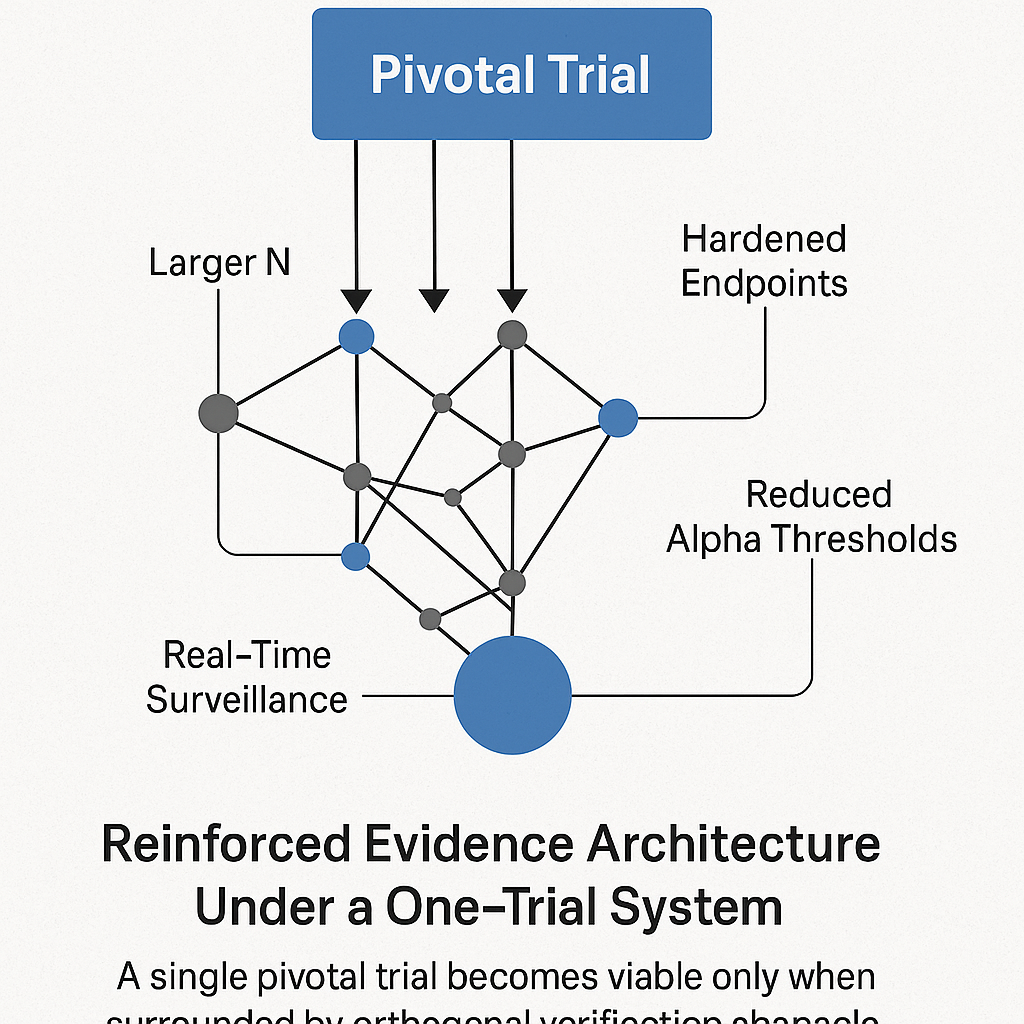
The FDA’s move to accept a single pivotal trial as “substantial evidence” marks the most consequential shift in U.S. regulatory architecture in decades. It accelerates innovation, lowers development cost, and aligns with federal pressure to reduce Medicare and Medicaid spending—programs that now consume nearly one-third of the U.S. federal budget.
But removing replication also removes the primary historical safeguard against statistical error. Under a one-trial system, the traditional p < 0.05 threshold is no longer defensible. Robustness must come from elsewhere: larger sample sizes, hardened endpoints, stricter alpha levels (p < 0.01), and real-time post-marketing surveillance capable of detecting inconsistencies across EHR data, claims, and manufacturer reports.
The policy is not intrinsically unsafe. What is unsafe is adopting it without recalibrating the statistical, operational, and surveillance architecture that once depended on trial duplication. A single pivotal trial can deliver truth—but only if the system surrounding it is rebuilt to withstand the loss of replication.
OMIDUBICEL AND THE LOGIC OF REGULATORY MATURATION
Omidubicel is not simply a “better cord blood product”; it is a partially activated hematologic platform that reorganizes the entire allogeneic transplant equation. Biologically, it combines the innate tolerance of umbilical cord blood with NAM-driven expansion of CD34+ progenitors, myeloablative “immune reset,” and controlled GVHD prophylaxis to deliver a high-dose, low-immunogenicity graft. This architecture accelerates neutrophil recovery, reduces severe infections, and maintains donor-derived malignancy risk within the historical allo-HSCT baseline, rather than creating a new safety problem.
Economically and humanly, Omidubicel monetizes engraftment efficiency: it shifts cost from chaotic ICU-driven complications to a high, predictable upfront product price. In young SAA patients, this produces a rational lifetime cost profile and compresses the window of maximum fear for patients and families, without romanticizing the brutality of HSCT itself. The unresolved axis is access. Without regional licensing and decentralized manufacturing, Omidubicel remains a high-price, low-volume therapy. With a deliberate licensing-out strategy, it can transition into a global platform that is biologically rational, clinically defensible, economically arguable, and ethically preferable across health systems.
Early Aspirin Withdrawal After PCI in Low-Risk Myocardial Infarction
In the post-PCI landscape shaped by new-generation drug-eluting stents, the antiplatelet decision is no longer a simple “DAPT by default” algorithm. The physician must evaluate a shifting pharmacodynamic hierarchy: aspirin provides limited incremental protection beyond the first month, while potent P2Y12 inhibition (ticagrelor or prasugrel) anchors the true anti-thrombotic effect. The modern question is not whether to withdraw aspirin, but when—and in which phenotype the balance between ischemic risk and bleeding liability makes early de-escalation both safe and structurally rational.
When Evidence Breaks: The Itvisma Approval, Novartis’ Faulty Reference, and the New SMA Power Hierarchy
Intrathecal delivery of onasemnogene abeparvovec requires a controlled lumbar puncture under sterile conditions, typically performed by a neurologist or anesthesiologist with experience in neuromuscular disorders. In older children and adolescents with SMA, the procedure enables direct vector exposure to spinal motor neurons while minimizing systemic AAV9 load. The clinical setting reflects the dual nature of the intervention: a one-time administration with the procedural complexity of a minor neurosurgical act and the transformative potential of gene replacement therapy.
The Structural Incompleteness of the modRNA Influenza Vaccine:Long-Term Safety Blindness, Inferential Fragility, and a Critical Immunogenicity Failure
The modRNA influenza platform shows statistical promise but remains structurally incomplete. Its biological half-life is unknown, its long-term immunologic consequences uncharacterized, and its efficacy estimate marked by severe inferential instability. Most critically, the vaccine fails to achieve noninferiority for influenza B, leaving a foundational gap in quadrivalent coverage. Until these structural deficiencies are resolved, the technology cannot be considered a reliable seasonal replacement.
Redefining Hemodynamic Strategy: How the EVERDAC Trial Resets the Standard of Care in Shock Management
Shock is not a blood-pressure problem — it is a perfusion failure. For decades, medicine responded to this failure with reflexive invasiveness, assuming that earlier arterial lines and tighter numerical control would save lives. The EVERDAC Trial dismantles that doctrine: critically ill patients in shock do just as well without early invasive catheterization, while avoiding the complications it introduces. The paradigm is shifting from procedure-first to physiology-first — restoring tissue oxygenation, guiding treatment with ultrasound, and reserving invasive tools only when the physiology demands them.
Beta-Blockers after Myocardial Infarction: When Physiologic Logic Outlives Clinical Reality
The 2025 New England Journal of Medicine pooled analysis marks the end of a 50-year reflex in cardiology. Among more than 17 800 patients who survived myocardial infarction with a preserved left-ventricular ejection fraction (≥ 50 %), beta-blocker therapy no longer conferred protection against death, recurrent infarction, or heart-failure hospitalization.
For decades, sympathetic blockade was viewed as an indispensable safeguard against electrical instability and sudden death. Yet in the modern reperfusion era—where nearly every patient receives stenting, dual antiplatelet therapy, statins, and renin–angiotensin inhibition—the old logic has dissolved. The drug’s physiologic rationale remains intact, but its clinical necessity has vanished.
Economically, this correction reshapes a USD 10 billion global class: up to 5 % of routine post-MI prescriptions will disappear, freeing hundreds of millions in low-value expenditure. What endures are the genuine indications—heart failure, arrhythmia, ischemic control—while medicine itself transitions from habitual protection to functional precision.
PSA Screening: Detection Without Prevention
The prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test was once hailed as a revolution in early cancer detection. Yet its promise of prevention has collapsed under the weight of biological ambiguity. PSA levels rise not only in malignancy but also in benign hyperplasia and inflammation, blurring the line between vigilance and harm. A normal prostate secretes small amounts of PSA into the bloodstream; as the gland enlarges or becomes cancerous, disruption of tissue architecture releases larger quantities. However, this increase is neither linear nor specific. Many men with elevated PSA never develop cancer, while some with aggressive disease show normal values.
The test thus measures disruption, not malignancy. It detects activity within the prostate but cannot distinguish its meaning. This diagnostic paradox—precision without discrimination—defines the core epistemic flaw of PSA screening: it finds disease where risk is low and often misses where risk is real.
FDA Removes the "Bridge Trial" Requirement for Biosimilars: Regulatory and Economic Implications
The Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) stands at the intersection of affordability, innovation, and public trust in the age of biosimilars.
Through the combined oversight of the FDA and the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), HHS is now redefining how biologic equivalence is validated—not merely through clinical replication, but through structural, molecular, and economic coherence.
Biosimilars represent both a scientific triumph and a fiscal experiment: the ability to reproduce the therapeutic precision of originator biologics at lower cost, without eroding confidence or safety.
Under the 2025 guidance removing the “bridge trial” requirement, HHS moves toward a total-evidence framework, where analytical comparability and real-world pharmacovigilance replace redundant human trials.
This shift marks a new philosophy of governance: trust in molecular data, anchored by post-market integrity.
It is not deregulation, but reallocation—an evolution from procedural proof to structural truth.