T-DXd + Pertuzumab Redefines First-Line HER2+ Therapy: Quantitative Supremacy, Structural Risk
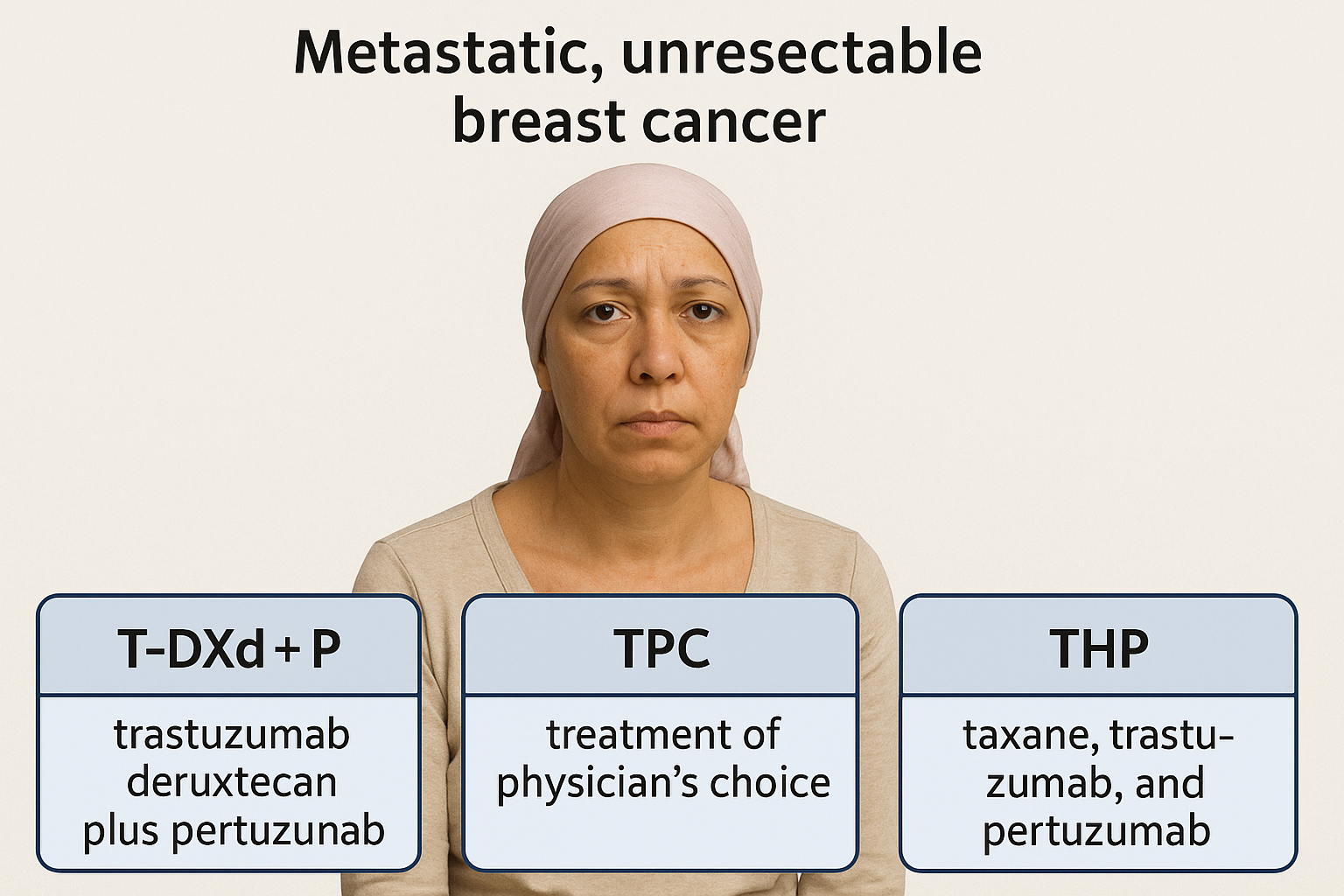
In the quiet space between diagnosis and decision, a woman with metastatic, unresectable HER2-positive breast cancer confronts three divergent paths.
On one side, the long-familiar THP regimen — taxane, trastuzumab, and pertuzumab — the cornerstone of a decade’s treatment.
In front of her, the new architecture of antibody–drug conjugates: trastuzumab deruxtecan (T-DXd) plus pertuzumab, a design where cytotoxic precision replaces the blunt force of chemotherapy.
And to the third path, the unblinded promise of T-DXd monotherapy — still in shadow, awaiting full revelation.
Each arm is more than a protocol. It is a symbol of how oncology now defines hope:
by balancing efficacy against toxicity, progress against opacity, and survival against the integrity of truth revealed in stages.
Annex 1 — Pharmacological Composition and Adverse-Event Profiles
Annex 2 — Early-Phase Clinical Evidence of Trastuzumab Deruxtecan (Phase 1 and 2)
Annex 3 — Pharmacoeconomic Impact and Health-System Integration Forecast
Annex 4 — Financial and Strategic Market Impact (AstraZeneca & Daiichi Sankyo)
Restoration of Central Vision With the PRIMA System
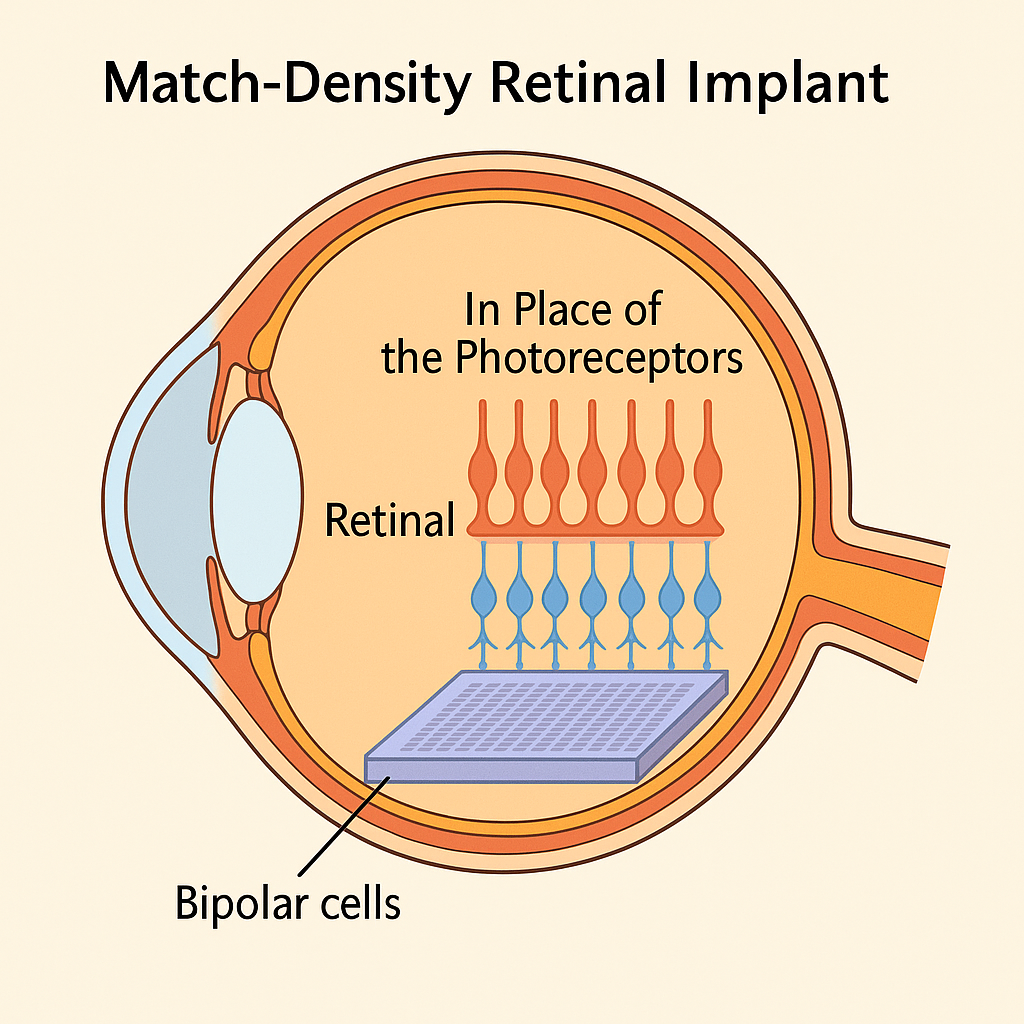
The PRIMAvera trial, published in NEJM (2025), demonstrates for the first time that a subretinal photovoltaic implant can restore central vision in patients with advanced dry AMD. At 12 months, 81% of evaluable patients achieved clinically meaningful visual gains, including word and number recognition. Yet the success rate falls closer to 65–70% on an intention-to-treat basis, revealing a structural gap between published efficacy and enrolled reality.
The deeper lesson lies beyond today’s results: the human retina has ~25–30,000 bipolar neurons per mm², while the PRIMA chip offers only ~95 electrodes/mm². Semiconductor technology could easily deliver millions of pixels, but overcrowding would cause thermal and electrochemical damage without adding useful vision. The future is not about raw density but about matching electrode arrays to biological capacity. By aligning implant design with natural limits—and leveraging blinking, pupillary reflex, and cortical plasticity—retinal prosthetics may finally cross from experimental restoration to functional daily use.
Annex Title: Biological Match Design for Subretinal Nano-Fabrication
Common Diseases, Hidden Rarities: The 3% Logic That Challenges the 97%
A recent NEJM study (Rahimov et al., 2025) revealed that up to 3% of patients diagnosed with common diseases such as multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel disease, or atopic dermatitis in fact harbor rare monogenic disorders. These hidden cases distort clinical trial outcomes, dilute efficacy signals, and misdirect patient care. The paradox is evident: to capture a small minority, one must consider testing the entire majority. Yet the rational solution is stratification — sequencing reserved for non-responders or applied during biopsy-confirmed disease. This approach reduces costs by two-thirds, triples cost-effectiveness, and maintains clinical integrity. In clinical trials, genetic screening as an inclusion criterion yields smaller but purer cohorts, while regulators will demand strict SAE oversight and 3–5 years of enhanced pharmacovigilance post-launch. Precision becomes sustainable only when anchored to feasibility.
Annex 1 — The Diagnostic Journey
Annex 2 — Health Economics of Sequencing
Annex 3 — Genetic Screening as an Inclusion Criterion
Elecsys pTau181: FDA Approval, Clinical Promise or Structural Market Expansion?
On October 13, 2025, the FDA approved Roche and Eli Lilly’s Elecsys pTau181 blood test, marking the second regulatory clearance of a blood-based assay for Alzheimer’s disease, following Fujirebio’s earlier approval in May. The Elecsys test, designed for adults over 55 with cognitive complaints, measures phosphorylated tau181 in plasma and is intended as a rule-out tool rather than a confirmatory diagnostic.
Clinical data show a negative predictive value (NPV) of 97.9%, allowing physicians to reliably exclude Alzheimer’s pathology in primary care. However, specificity remains limited at ~70%, restricting its standalone diagnostic utility. While the test does not modify therapeutic decisions—treatment initiation still requires PET or CSF confirmation—it creates a scalable entry point into everyday practice.
From a structural perspective, Elecsys embodies the tension between clinical necessity and industrial expansion: marketed as democratization of diagnosis, yet strategically positioned to embed Roche’s Elecsys platform into routine workflows, potentially inflating healthcare costs through repeat testing and downstream imaging.
Annex 1 — Alzheimer’s Disease
Annex 2 — Technical Basis of the Elecsys pTau181 Blood Test
Annex 3 — Related Patent Landscape with Expiry Dates
Annex 4 — Potential Market Size and Estimated Revenue
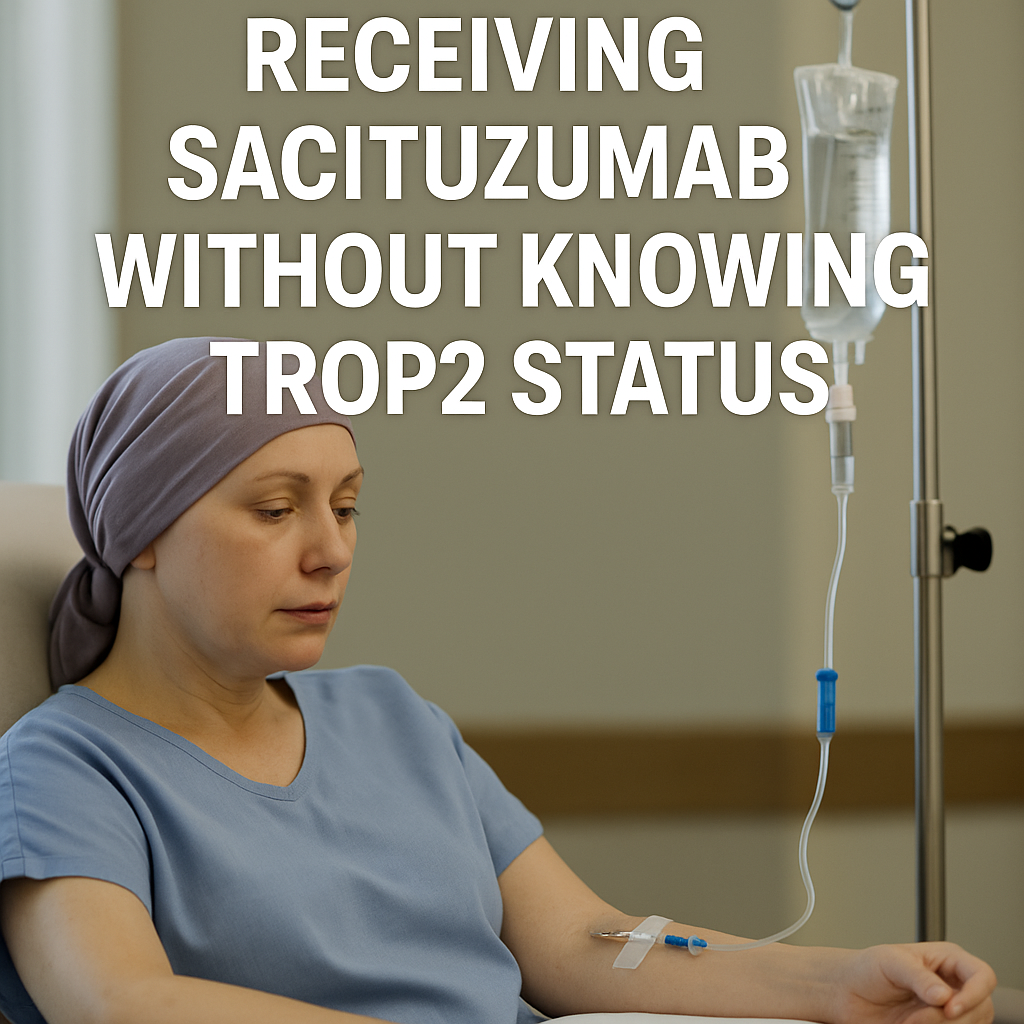
Sacituzumab Tirumotecan in EGFR-Resistant NSCLC: A Two-Layer Integrity Analysis
The clinical development of sacituzumab tirumotecan (SKB264) illustrates a profound contradiction between scientific promise and ethical responsibility. While early-phase studies generated signals of efficacy in EGFR-mutant NSCLC, the absence of prospective TROP2 confirmation represents a fundamental breach of clinical and research standards. Biopsy-based molecular profiling is routine worldwide in NSCLC; to proceed without confirming the presence of the drug’s target exposed patients to risk without a reasonable expectation of benefit.
Moreover, the inflated enrollment in phase 1/2 (over 1,400 patients across >100 centers) contrasted with the China-only pivotal phase 3 (~356–480 patients) creates a transparency gap. The large discrepancy between subjects enrolled and those reported in publications leaves open the possibility of selective reporting and statistical manipulation. Together, these design flaws compromise both the ethical and epistemic integrity of the SKB264 program.
BBIU concludes that this is not simply a matter of methodological weakness but a systemic ethical lapse: patient rights to informed consent, standard of care, protection from harm, scientific integrity, and equal treatment have been compromised. Regulatory shortcuts—accepted under FDA IND flexibility in early phases and then restricted to NMPA approval in China—magnify the credibility gap.
Annex 1 — BBIU Regulatory Due-Diligence Checklist for ADC Trials
Annex 2 — Ethical Violations and Patient Rights Breaches in SKB264 Trials
Restoring Hearing Through Otoferlin Gene Therapy: Structural Implications of DB-OTO Trial
The DB-OTO trial (NEJM, 2024) shows first evidence that congenital deafness from OTOF mutations can be partially reversed. Children treated with a dual-AAV cochlear injection recovered auditory responses within weeks. This is a milestone in sensory gene therapy, but early framing overstated efficacy: the protocol’s primary endpoint is safety, not hearing restoration. With <15 patients so far, long-term risks and durability remain unknown.
Annex 1 — Otoferlin Biology and Clinical Translation
Annex 2 — Dual AAV and Immune Risks
CDC’s Retreat from Universal COVID Vaccination: Structural Implications for Public Health Trust
On October 7, 2025, the CDC made a historic change to its immunization schedule: COVID-19 vaccines are no longer universally recommended for all Americans six months and older. Instead, vaccination is now an individual decision, to be made in consultation with a physician.
At the same time, the CDC adjusted pediatric guidelines: toddlers will now receive separate MMR and varicella shots rather than the combined MMRV, after studies showed a slightly higher risk of febrile seizures with the combo dose.
The shift reflects a broader recalibration of U.S. public health policy—from blanket mandates toward individualized consent—amid political reshaping of the CDC’s advisory committee and declining public confidence in universal vaccine strategies.
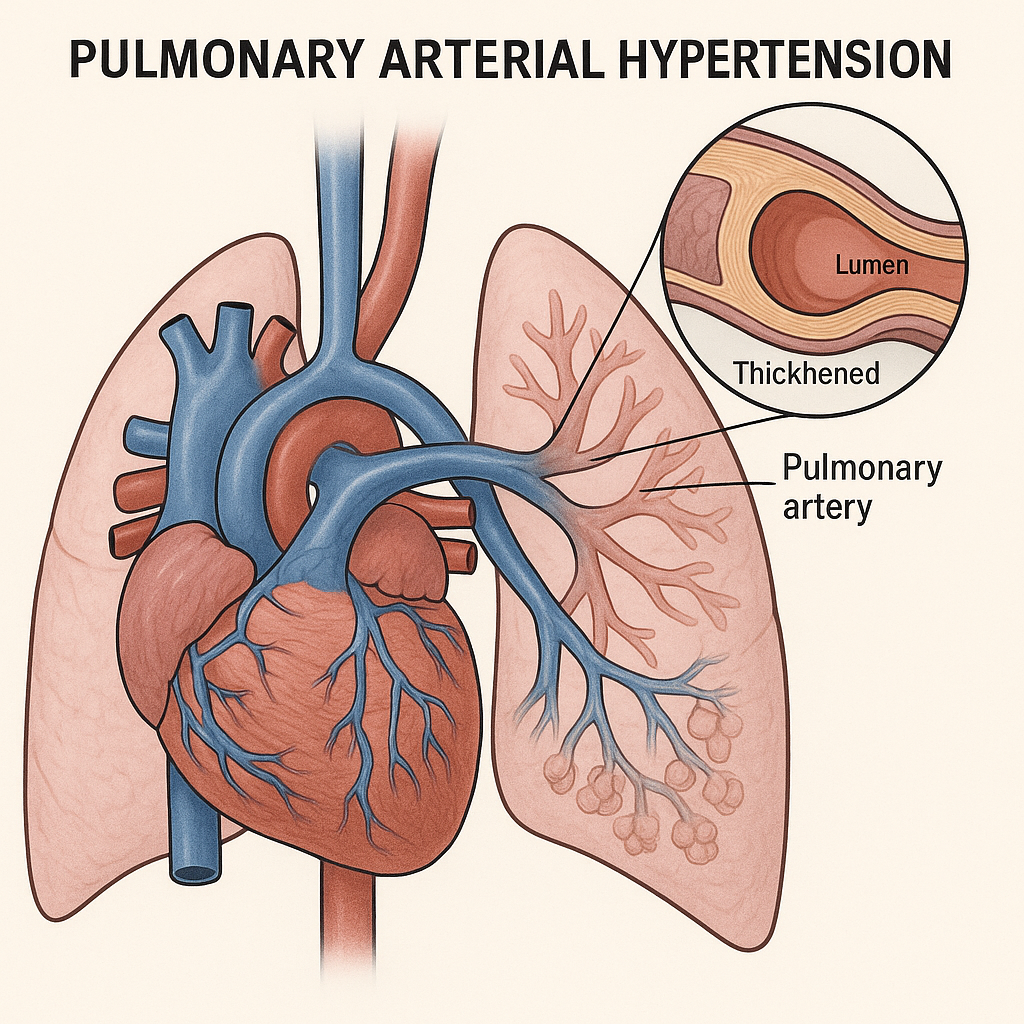
Sotatercept in Early Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Structural Reassessment of Therapeutic Onset
What’s new (NEJM, Sept 30, 2025; HYPERION, NCT04811092).
First Phase 3 use of sotatercept within ≤12 months of PAH diagnosis on top of dual/triple therapy. Primary endpoint met: clinical worsening 10.6% vs 36.9%; HR 0.24 (95% CI 0.14–0.41; P<0.001). Fewer hospitalizations (1.9% vs 8.8%) and exercise deterioration (5.0% vs 28.8%); mortality neutral at 1 year. Trial stopped early for loss of equipoise.
Why it matters.
Sotatercept shifts from late “rescue” to early disease-modifying anchor, likely pressuring guidelines, payers, and treatment algorithms.
Annex 1 (Pathophysiology) — One-page gist
Annex 2 (Sotatercept Pharmacology) — Essentials
Annex 3 (Pharmacoeconomics) — Bottom line
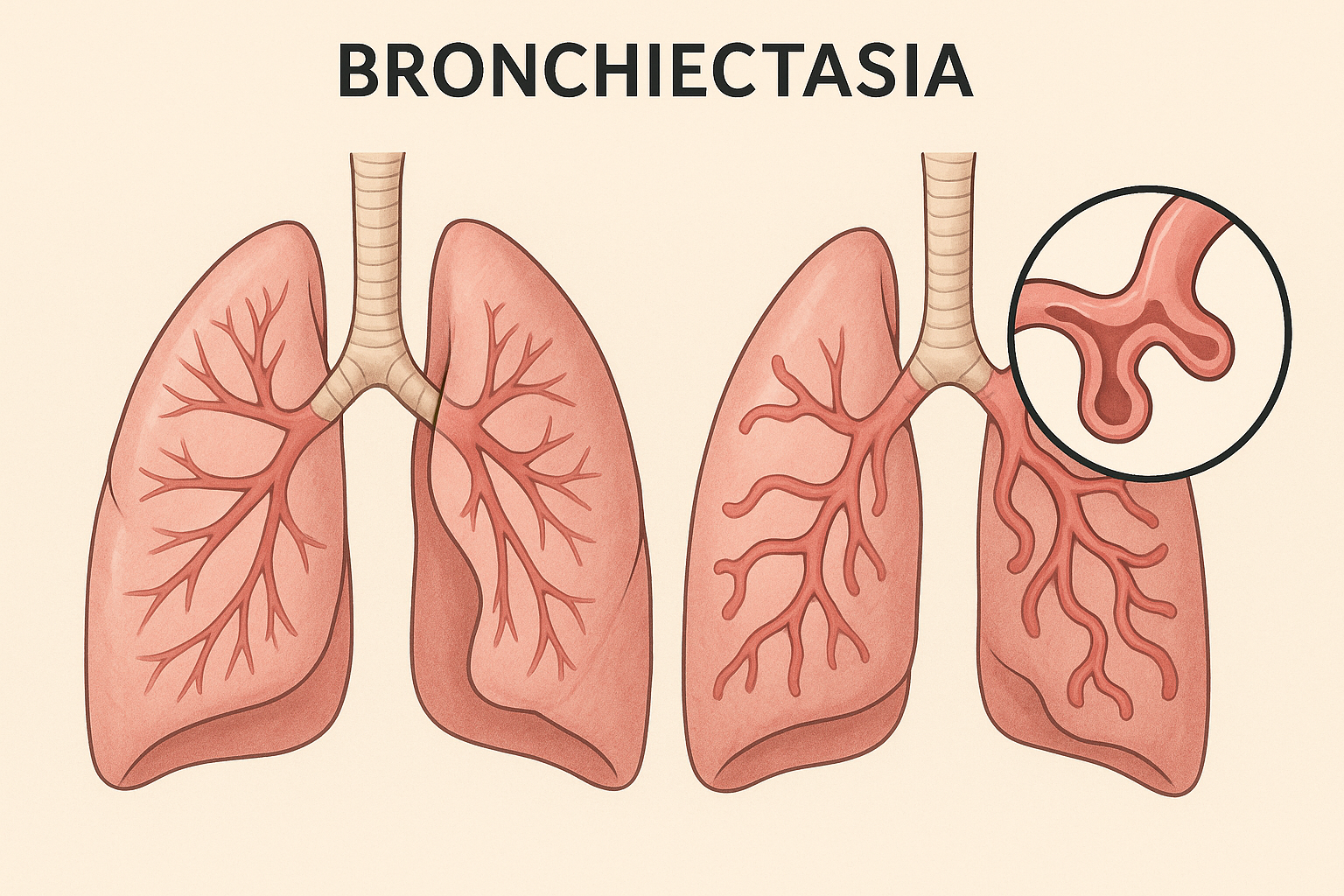
NEJM Trial on Mucoactive Therapies in Bronchiectasis: Structural Reassessment of Clinical Value
Trial at a glance (CLEAR, NEJMoa2510095).
Multicenter UK, 2×2 factorial, n=288, 52-week follow-up. Interventions: 6% hypertonic saline (inhaled) and carbocisteine (oral) vs standard care.
Primary outcome: annualized exacerbations — no significant reduction (adj. Δ: saline −0.25; carbocisteine −0.04).
Secondaries: no consistent benefit in QoL, lung function, or time-to-exacerbation. Safety acceptable.
Implication.
Guideline habit of universal mucoactive use in non-CF bronchiectasis is structurally weakened; shift toward selective, symptomatic use rather than routine prescription.
Annex Snapshot — Technical Evidence Base (Key Points)
Inhaled Heparin: An Old Anticoagulant Emerging as a New Weapon Against Severe Respiratory Infections
What’s new. A multinational meta-trial (eClinicalMedicine, 2025) found nebulized unfractionated heparin cut the combined risk of intubation or death by ~50% in hospitalized COVID-19 patients versus standard care—reigniting interest in a cheap, stockpiled therapy.
Why it matters. Current tools are fragmented (early antivirals, broad steroids, pricey biologics). Inhaled heparin concentrates action in the lungs with minimal systemic exposure, making it attractive for low- and middle-income settings and surge waves.
How it works (multi-pathway).
Anticoagulant: counters pulmonary microthrombosis.
Anti-inflammatory & endothelial protection: stabilizes the alveolar–capillary barrier.
Antiviral decoy: can bind spike proteins and impede entry.
Safety/unknowns. Generally reassuring with inhalation (lower systemic absorption → lower HIT risk), but dose, schedule, and bleeding surveillance need Phase III confirmation.
Mini-Annex (snapshots).
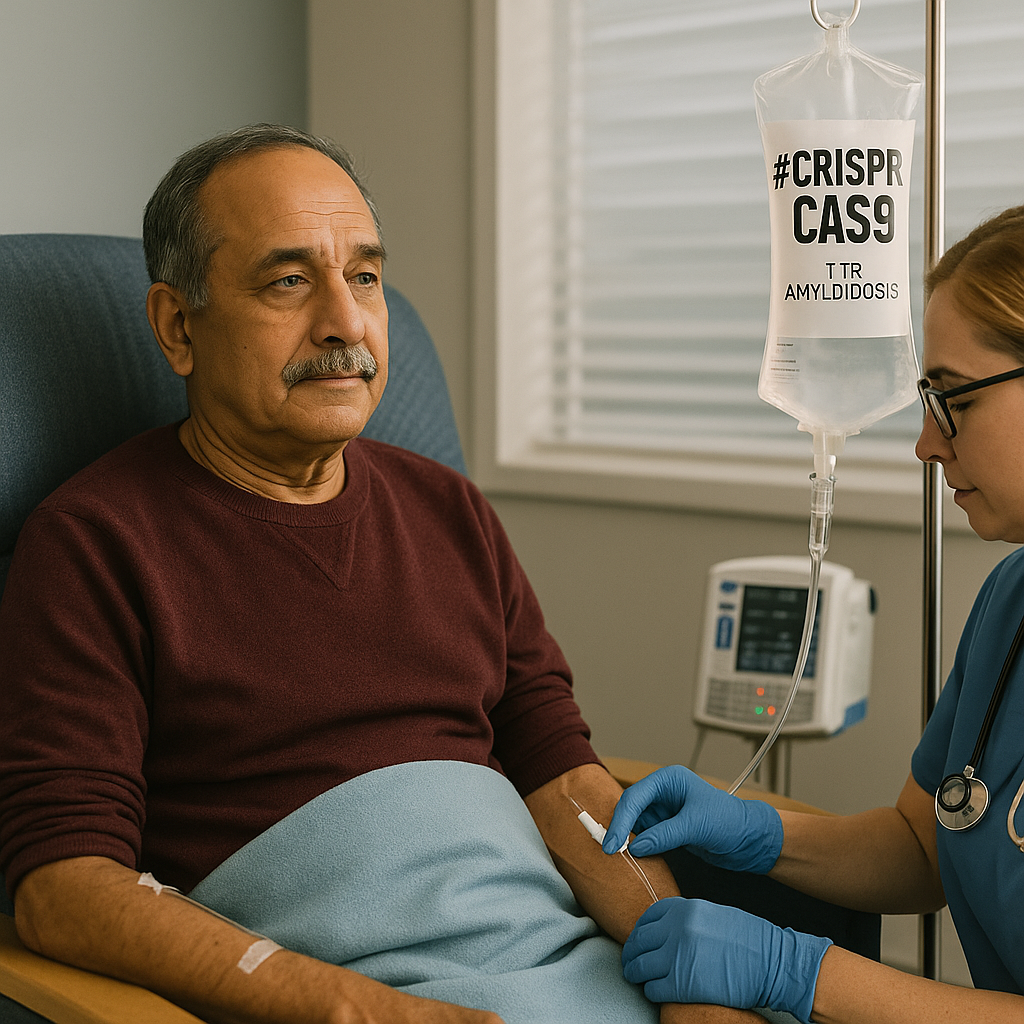
Nexiguran Ziclumeran Gene Editing in Hereditary ATTR with Polyneuropathy
The NEJM trial of nexiguran ziclumeran (NTLA-2001) marks the first demonstration of systemic in vivo CRISPR editing in humans. By targeting hepatic TTR production, patients with hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis achieved >90% median serum TTR knockdown and stabilization of neuropathy scores. While safety signals were generally favorable, the study’s early-phase design leaves key uncertainties: attribution of serious adverse events, long-term off-target effects, and the consequences of lifelong TTR silencing. Beyond ATTRv-PN, this trial symbolizes a turning point—patients act simultaneously as treatment recipients and pioneers in proving the feasibility of permanent gene editing for chronic disease.
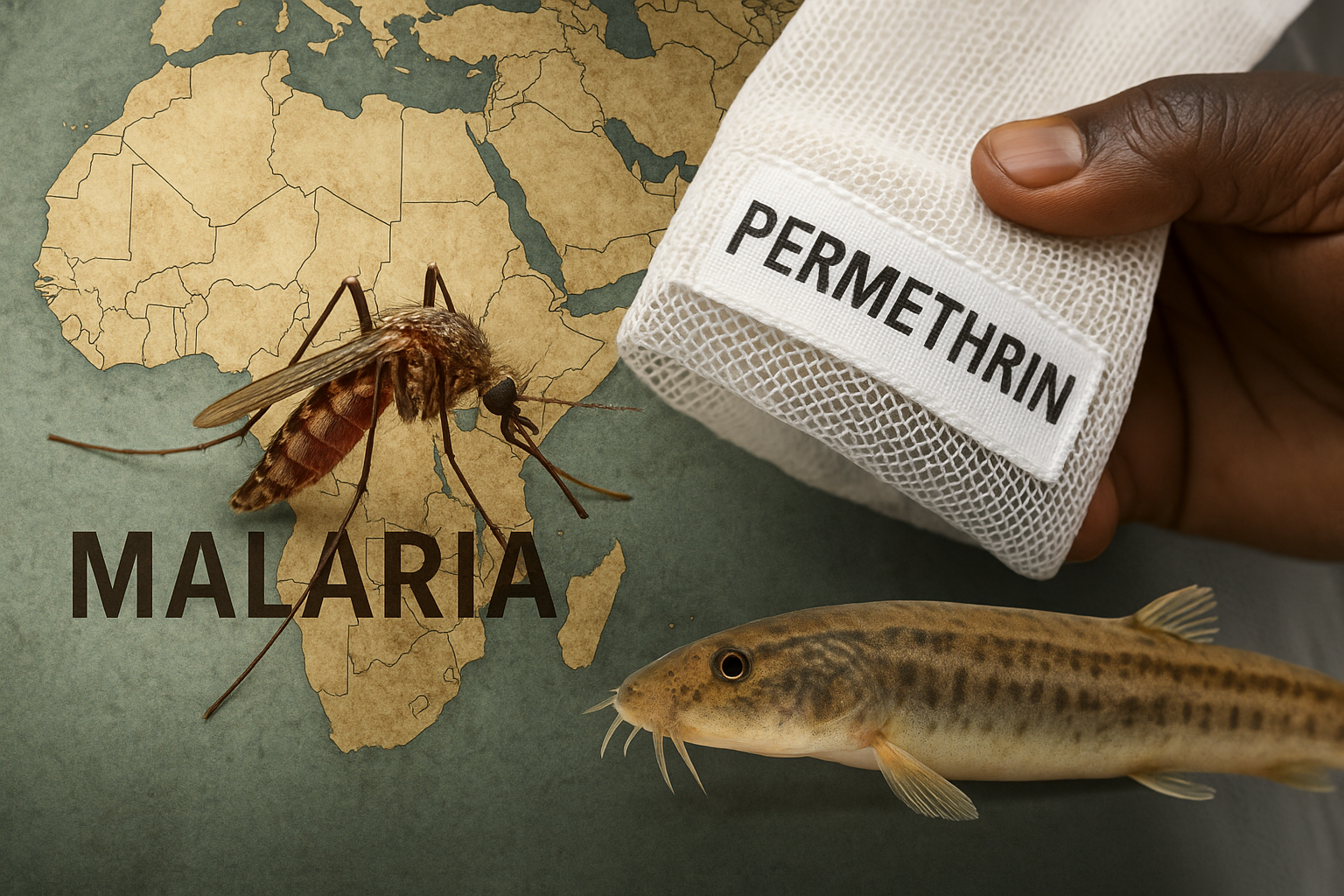
Permethrin-Treated Baby Wraps: An Experimental Shield Against Malaria
The NEJM trial on permethrin-treated baby wraps reveals both the promise and the peril of chemical vector control in Africa. While the wraps reduced malaria incidence among infants, their long-term use risks ecological toxicity and accelerated resistance in Anopheles mosquitoes. In contrast, the dojo loach (Misgurnus anguillicaudatus) offers a bioeconomic pathway: natural larval predation, improved community nutrition, and sustainable resilience. The future of malaria control will not be decided by chemistry alone, but by whether we choose dependency or ecological sovereignty.
FDA Blocks Biogen’s High-Dose Spinraza in the U.S.: A Regulatory Setback Driven by Manufacturing Controls
On September 23, 2025, the FDA issued a Complete Response Letter (CRL) rejecting Biogen’s high-dose Spinraza submission, not due to safety or efficacy, but because of deficiencies in Module 3 (CMC). This dossier, the cornerstone of manufacturing integrity, failed to convince regulators that the higher-dose formulation could be produced consistently and reliably at scale. The rejection highlights a structural miscalculation: Biogen’s decision to prioritize speed under commercial pressure, while leaving critical documentation incomplete. It is a reminder that in today’s regulatory landscape, the ultimate gatekeeper of therapeutic progress is not clinical promise, but manufacturing rigor.
Low-Dose Aspirin in PI3K-Altered Colorectal Cancer: From Observational Hints to Randomized Proof
From willow bark to genomic oncology, aspirin’s journey spans centuries. In 1763, Reverend Edward Stone tested the bitter powder of willow bark to relieve fever, unknowingly isolating the foundation of modern pharmacology. Two centuries later, the same compound re-emerges in precision medicine: low-dose aspirin, repurposed not for the masses but for a genetically defined subset of colorectal cancer patients carrying PI3K-pathway mutations. The continuity is striking—what began as rustic empirical observation now stands as randomized evidence in The New England Journal of Medicine. Yet the paradox remains: a pill that costs less than a coin can alter the trajectory of cancer recurrence, while at the same time demanding restraint, lest its indiscriminate use lead to hemorrhagic harm.
Tylenol, Pregnancy, and Autism Risk: Between Policy Shock and Scientific Ambiguity
Acetaminophen, long perceived as the “safest” option for pain and fever in pregnancy, is now at the center of regulatory and scientific controversy. The FDA’s recent announcement acknowledges a possible association between prenatal exposure and neurodevelopmental disorders, while new mechanistic studies point to hormonal disruption, epigenetic silencing, and oxidative stress in the developing fetal brain. The debate illustrates a deeper epistemic tension: how far precautionary policy should go when evidence is observational, contested, but biologically plausible.
Keytruda SC Approval: Alteogen’s ALT-B4 Transforms Oncology Administration into a One-Minute Therapy
The FDA approval of Keytruda QLEX™, the first subcutaneous formulation of pembrolizumab co-developed by Merck and Alteogen, marks more than a convenience upgrade. It is the structural reconfiguration of oncology: shifting from one-hour IV infusions to two-minute injections, from tertiary hospitals to community clinics, and from milestone payments to recurring global royalties. For Merck, it extends dominance beyond the 2028 patent cliff; for Alteogen, it validates a single Korean enzyme as the indispensable backbone of the world’s best-selling cancer drug.
Avian Influenza Returns to Minnesota: Turkey Industry Caught Between Containment and Vaccine Hopes
Avian influenza has returned to Minnesota, exposing once again the structural fragility of the poultry trade. Nearly 20,000 turkeys were culled in Redwood County, a reminder that lasers and biosecurity can delay but not prevent outbreaks. Farmers now pin their hopes on vaccination, yet no vaccine currently matches the dominant strain, and timelines remain uncertain.
This report delivers two layers of analysis: the main body concludes with the BBIU Opinion for readers seeking clarity and judgment, while extended Annexes provide definitions, economic models, and global trade context for those requiring full traceability.
FDA Warning on Imported Cookware: Regulation Exists, Enforcement Fails
In August 2025, the FDA issued a safety alert on imported cookware that leaches lead into food. This is not a case of weak regulation — U.S. law explicitly bans lead in food-contact surfaces. The real failure lies in global enforcement: contaminated products entered the retail chain, and in one case the importer could not even be identified, blocking a recall.
Lead poisoning, or saturnism, is an ancient disease in a modern disguise. Its symptoms are silent, its diagnosis depends on clinical suspicion, and its victims are often children, pregnant women, and low-income households. What was once the occupational disease of miners now reflects a deeper fragility: law without traceability is powerless, and globalization re-imports the toxic risks it once expelled.
Oral Semaglutide 25 mg – OASIS 4 Trial
The OASIS-4 trial introduces oral semaglutide 25 mg as a mid-tier obesity therapy, achieving a 13.6% weight reduction at 64 weeks in non-diabetic adults. While the oral route promises broader patient acceptance and reduced costs compared with injectables, the absence of serious adverse event reporting leaves critical gaps in safety transparency. When contrasted with CagriSema — which delivered ~20% weight loss in non-diabetic cohorts and ~13.7% in diabetic patients — OASIS-4 appears less a clinical breakthrough than a commercial positioning maneuver. Novo Nordisk is constructing a strategic portfolio ladder: high-efficacy injectables, high-dose oral, and now an intermediate oral dose to normalize GLP-1 use as a daily pill. This shift democratizes access but raises structural risks of adherence, efficacy trade-offs, and long-term dependency.
Pharma’s Domestic Reinforcement Wave: $5B Eli Lilly Virginia Plant and the $350B Pledge Cascade
Eli Lilly’s $5 billion Virginia plant is not an isolated corporate expansion, but part of a $350 billion wave of U.S. biopharma reshoring triggered by tariff threats and strategic signaling from Washington. While Big Pharma secures high-margin biologics inside U.S. borders, the chemical backbone of medicine—antibiotics, insulin, heparin—remains dangerously dependent on India and exposed to disruption. BBIU’s position is clear: biologics sovereignty protects profits, but API sovereignty protects lives.